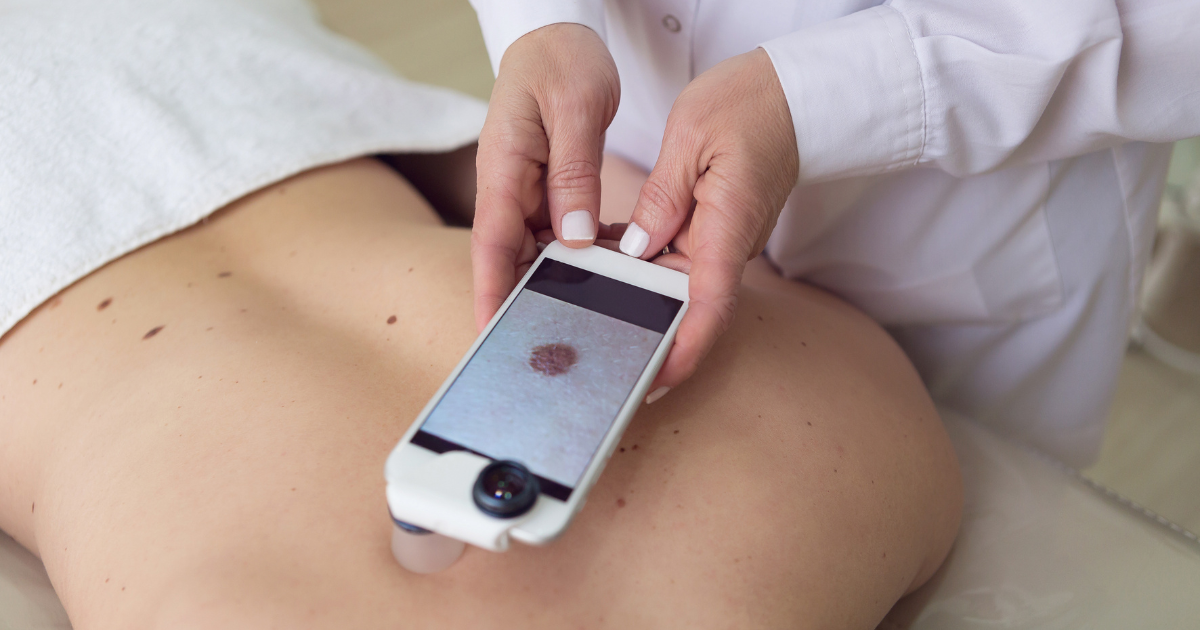
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. While melanoma accounts for only a small percentage of skin cancer cases, it is the most deadly form of the disease if not detected and treated early. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of melanoma is crucial for early detection and successful management of the disease. Here’s what you need to know about melanoma.
Causes of Melanoma:
The exact cause of melanoma is not fully understood, but several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These include:
- Excessive Sun Exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the most significant risk factor for melanoma. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can trigger the development of melanoma.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes are at higher risk of developing melanoma because they have less melanin to protect their skin from UV radiation.
- Family History: A family history of melanoma or other types of skin cancer increases the risk of developing the disease. Certain genetic mutations inherited from parents can also predispose individuals to melanoma.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients or those with HIV/AIDS, are at increased risk of developing melanoma.
Symptoms of Melanoma:
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body, including areas not exposed to the sun. It often appears as an abnormal mole or spot that changes in size, shape, color, or texture. Common signs and symptoms of melanoma include:
- A new mole or growth on the skin
- Changes in the size, shape, or color of an existing mole
- Irregular or asymmetrical borders of a mole
- Varied colors within a mole, such as shades of brown, black, blue, or red
- Itchiness, tenderness, or pain in a mole or lesion
- Bleeding or oozing from a mole
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, it’s essential to see a dermatologist promptly for evaluation and possible biopsy.
Treatments for Melanoma:
The treatment for melanoma depends on the stage of the disease, as well as the individual’s overall health and preferences. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the melanoma and a surrounding margin of healthy tissue is the primary treatment for early-stage melanoma. In some cases, a sentinel lymph node biopsy may be performed to determine if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy drugs help the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. These drugs may be used alone or in combination with other treatments to treat advanced melanoma or prevent recurrence.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs target specific genetic mutations or proteins present in melanoma cells, blocking their growth and spread. These drugs are used to treat advanced melanoma that has spread to other parts of the body.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs may be used to kill cancer cells or slow their growth in advanced melanoma that has spread to distant organs or lymph nodes.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams of radiation to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. It may be used to treat melanoma that has spread to the brain or other areas of the body.
Prevention of Melanoma:
While not all cases of melanoma can be prevented, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the disease:
- Limit exposure to UV radiation from the sun, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Wear protective clothing, including hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts, when outdoors.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps, which emit harmful UV radiation.
- Perform regular skin self-exams to monitor moles and other skin changes, and see a dermatologist annually for a full-body skin check.
Conclusion:
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment for the best possible outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of melanoma, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this potentially deadly disease. Practice sun safety, perform regular skin self-exams, and see a dermatologist promptly if you notice any concerning changes in your skin. Early detection and treatment are key to successful outcomes in melanoma, so don’t delay seeking medical attention if you have any concerns about your skin health.